''AMA'' CONCEPT IN AYURVEDA..
AMA CONCEPT IN AYURVEDA..
In Ayurveda, "Ama" (pronounced as "ah-ma") refers to the accumulation of toxins or undigested food residues in the body. It is considered one of the root causes of various health issues according to this ancient Indian holistic healing system. The concept of Ama is crucial to understanding how imbalances in the body can lead to disease and discomfort.
Here's a breakdown of the concept of Ama in Ayurveda:
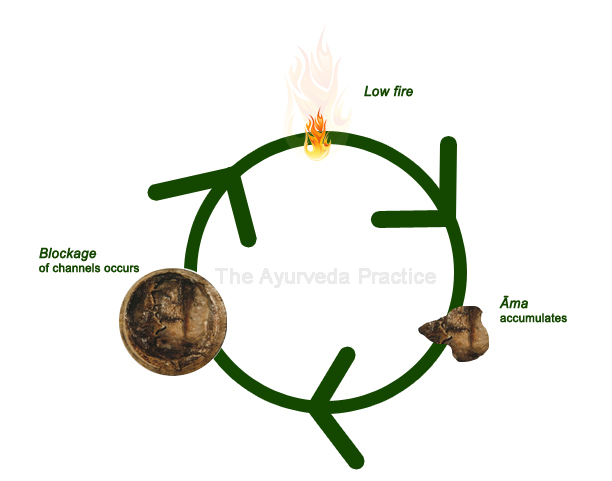
1.Digestive Agni: Ayurveda places a significant emphasis on the strength of the digestive fire or "Agni," which is responsible for the proper digestion and assimilation on food. When Agni is weak or impaired, it fails to digest food completely, leading to the formation of Ama.
2.Toxic Residue: Ama is thought to be a sticky, toxic, and malodorous substance that results from improperly digested food. It is said to clog the channels of the body (srotas), obstructing the smooth flow of energy (prana), nutrients, and waste removal.
3.Causes: Ama can arise due to various factors, including poor dietary choices, overeating, eating incompatible food combinations, weak Agni, irregular eating habits, and emotional disturbances.
4.Symptoms: The accumulation of Ama in the body can manifest in a wide range of symptoms, such as fatigue, heaviness, lethargy, bad breath, coated tongue, poor appetite, digestive issues, body aches, and a weakened immune system.
5. Detoxification and Prevention: Ayurveda places a strong emphasis on the prevention and removal of Ama from the body. Detoxification practices, known as "Panchakarma," are employed to eliminate toxins and restore balance. These may include various cleansing techniques, herbal therapies, massages, and dietary adjustments.
6. Balancing Agni: Strengthening and balancing Agni is essential in preventing the formation of Ama. Ayurveda recommends mindful eating, consuming easily digestible foods, avoiding incompatible food combinations, and following a daily routine to support healthy digestion.
7. Herbal Remedies: Ayurvedic herbs are often used to treat Ama and enhance digestive function. Some commonly used herbs include ginger, turmeric, triphala, fennel, and cumin.
8. Mind-Body Connection: Ayurveda acknowledges the strong connection between the mind and body. Emotional disturbances and stress can impact Agni and contribute to the formation of Ama. Therefore, practices like meditation, yoga, and pranayama (breathwork) are encouraged to promote overall well-being.
By addressing the concept of Ama, Ayurveda aims to maintain or restore balance in the body and mind, thus supporting optimal health and vitality. It is important to note that Ayurvedic principles and practices should be followed under the guidance of a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner to ensure individualized and safe approaches to health and healing.









Comments
Post a Comment